Complete Graphs
From G-designs
Relevant articles: [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], [22], [23].
Contents[hide] |
Complete Graphs
In this section the complete graph on 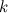 vertices, denoted
vertices, denoted 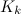 , is considered. A
, is considered. A 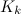 -design of order
-design of order 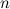 is better known as a
is better known as a 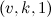 -BIBD with
-BIBD with 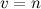 .
.
Spectrum Results
For 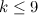 , Table 1 summarises the known results on the spectrum problem for
, Table 1 summarises the known results on the spectrum problem for 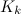 . An explanation of the sources of these results is given in [7].
. An explanation of the sources of these results is given in [7].
Table 1
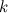
| Spectrum for 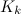
| Possible exceptions |
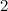
| 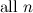
| 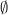
|
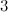
| 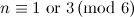
| 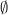
|
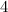
| 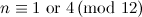
| 
|
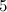
| 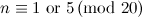
| 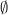
|
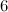
| 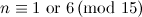
| 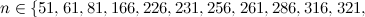
|

| 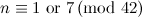
| 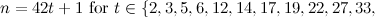
|
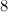
| 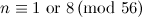
| 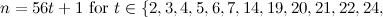
|
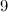
| 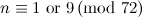
| 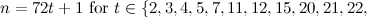
|
For 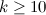 , the known
, the known 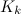 -designs are given by Theorem 1 (and Wilson's Theorem).
-designs are given by Theorem 1 (and Wilson's Theorem).
Theorem 1
Let 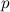 be a prime power and let
be a prime power and let 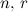 and
and  be integers such that
be integers such that 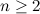 and
and 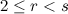 .
.
- There exists a
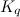 -design of order
-design of order 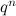 (affine geometries) (see [22]).
(affine geometries) (see [22]).
- There exists a
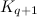 -design of order
-design of order 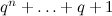 (projective geometries) (see [22]).
(projective geometries) (see [22]).
- There exists a
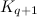 -design of order
-design of order 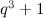 (unital designs) (see [8]).
(unital designs) (see [8]).
- There exists a
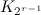 -design of order
-design of order 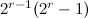 (oval designs) [9].
(oval designs) [9].
- There exists a
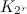 -design of order
-design of order 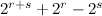 (Denniston designs) [13].
(Denniston designs) [13].
Obvious necessary conditions for the existence of a 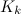 -design of order
-design of order 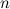 are
are
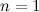 or
or 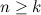 ;
;
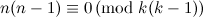 ; and
; and
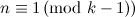 .
.
Further necessary conditions for the existence of a 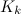 -design of order
-design of order 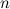 are described in the following three theorems.
are described in the following three theorems.
Theorem 2 [14]
There is no 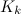 -design of order
-design of order 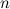 for any
for any 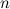 in the range
in the range 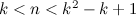 .
.
Theorem 4 [20]
There is no 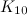 -design of order
-design of order 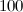 and no
and no 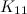 -design of order
-design of order 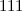 .
.
Notes
- A
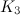 -design is a Steiner triple system.
-design is a Steiner triple system.
References
- ↑ Abel, R. J. R. Some new BIBDs with λ=1 and 6\leq k\leq 10, J. Combin. Des. 4, 27–50 (1996).
- ↑ Abel, R. J. R., Bluskov, I., Greig, M., and de Heer, J. Pair covering and other designs with block size 6, J. Combin. Des. 15, 511 (2007).
- ↑ Abel, R. J. R. and Greig, M. BIBDs with small block size, CRC Press Series on Discrete Mathematics and its Applications, The CRC handbook of combinatorial designs, ed. 1, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 41–47 (1996).
- ↑ Abel, R. J. R. and Greig, M. Some new RBIBDs with block size 5 and PBDs with block sizes \equiv 1\bmod 5, Australas. J. Combin. 15, 177–202 (1997).
- ↑ Abel, R. J. R. and Greig, M. BIBDs with small block size, CRC Press Series on Discrete Mathematics and its Applications, The CRC handbook of combinatorial designs, ed. 2, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 72–79 (2007).
- ↑ Abel, R. J. R. Some new BIBDs with block size 7, J. Combin. Des. 8, 146–150 (2000).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Adams, P., Bryant, D., and Buchanan, M. A survey on the existence of G-designs, J. Combin. Des. 16, 373–410 (2008).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Assmus Jr., E. F. and Key, J. D. Designs and their codes, Cambridge Tracts in Mathematics, Vol. 103, Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, (1992).
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Bose, R. C. and Shrikhande, S. S. On the construction of sets of mutually orthogonal Latin squares and the falsity of a conjecture of Euler, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 95, 191–209 (1960).
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Bruck, R. H. and Ryser, H. J. The nonexistence of certain finite projective planes, Canadian J. Math. 1, 88–93 (1949).
- ↑ Buratti, M. and Zuanni, F. $G-invariantly resolvable Steiner 2-designs which are 1-rotational over G, Bull. Belg. Math. Soc. Simon Stevin, 5, 221–235 (1998).
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Chowla, S. and Ryser, H. J. Combinatorial problems, Canadian J. Math. 2, 93–99 (1950).
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Denniston, R. H. F. Some maximal arcs in finite projective planes, J. Combinatorial Theory, 6, 317–319 (1969).
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Fisher, R. A. An examination of the different possible solutions of a problem in incomplete blocks, Ann. Eugenics, 10, 52–75 (1940).
- ↑ Greig, M. Recursive constructions of balanced incomplete block designs with block size of 7, 8 or 9, Ars Combin. 60, 3–54 (2001).
- ↑ Hanani, H. The existence and construction of balanced incomplete block designs, Ann. Math. Statist. 32, 361–386 (1961).
- ↑ Houghten, S. K., Thiel, L. H., Janssen, J., and Lam, C. W. H. There is no (46,6,1) block design, J. Combin. Des. 9, 60–71 (2001).
- ↑ Janko, Z. and Tonchev, V. D. New designs with block size 7, J. Combin. Theory Ser. A, 83, 152–157 (1998).
- ↑ Kirkman, T. P. On a problem in combinations, Cambridge and Dublin Math. J. 2, 191–204 (1847).
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Lam, C. W. H., Thiel, L., and Swiercz, S. The nonexistence of finite projective planes of order 10, Canad. J. Math. 41, 1117–1123 (1989).
- ↑ Mills, W. H. BIBDs with k=6 and λ=1, Math. Appl. Computational and constructive design theory, Kluwer Acad. Publ. Dordrecht, 189–226 (1996).
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 Wallis, W. D. Combinatorial designs, Monographs and Textbooks in Pure and Applied Mathematics, Vol. 118, New York:Marcel Dekker Inc. (1988).
- ↑ Wilson, R. M. Decompositions of complete graphs into subgraphs isomorphic to a given graph, Proceedings of the Fifth British Combinatorial Conference (Univ. Aberdeen, Aberdeen, 1975), Congressus Numerantium, No. XV, Utilitas Math., Winnipeg, Man. 647–659 (1976).
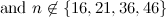
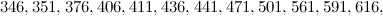
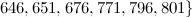
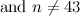
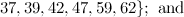
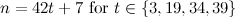
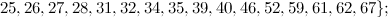
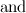
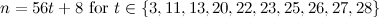
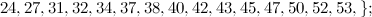
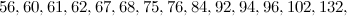
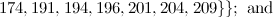
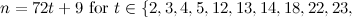
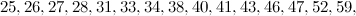
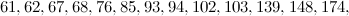
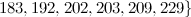
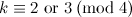 and
and 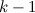 is not the sum of two integer squares then there is no
is not the sum of two integer squares then there is no 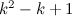 and no
and no 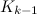 -design of order
-design of order 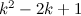 .
.