Graphs with five vertices
From G-designs
Relevant articles: [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18].
Contents[hide] |
Graphs with five vertices
There are  non-isomorphic graphs with five vertices, excluding those with isolated vertices, and these are shown in Figure 1.
non-isomorphic graphs with five vertices, excluding those with isolated vertices, and these are shown in Figure 1.
Spectrum Results
Table 1
summarises the known results on the spectrum problem for graphs with
five vertices. An explanation of the sources of these results is given
in [1].
In addition to the results described in [1], the following results have been obtained:-
 -designs of orders
-designs of orders 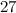 ,
, 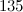 ,
, 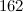 and
and 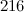 were constructed in [12].
were constructed in [12].
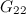 -designs of orders
-designs of orders 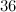 ,
, 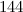 and
and 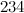 were constructed in [18].
were constructed in [18].
The last remaining open cases for 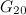 -designs,
-designs, 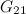 -designs, and
-designs, and 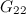 -designs have now all been settled, [13].
-designs have now all been settled, [13].
Table 1
| Graph | Spectrum | Possible exceptions |
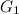
| 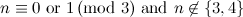
| 
|
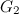
| 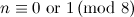
| 
|
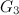
| 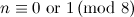
| 
|
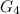
| 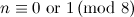
| 
|
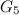
| 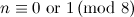
| 
|
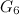
| 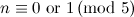
| 
|
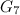
| 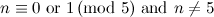
| 
|
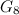
| 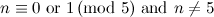
| 
|
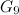
| 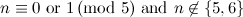
| 
|
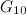
| 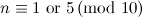
| 
|
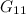
| 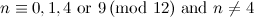
| 
|
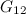
| 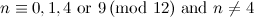
| 
|
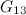
| 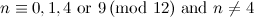
| 
|
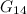
| 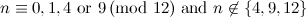
| 
|
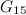
| 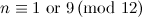
| 
|
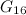
| 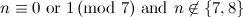
| 
|
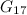
| 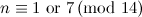
| 
|
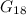
| 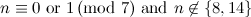
| 
|
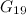
| 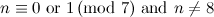
| 
|
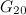
| 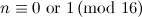
| 
|
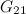
| 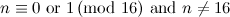
| 
|
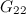
| 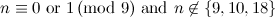
| 
|
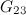
| 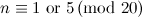
| 
|
Notes
- Note that
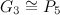 is a path,
is a path, 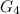 is a caterpillar,
is a caterpillar, 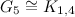 is a star,
is a star, 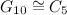 is a cycle and
is a cycle and 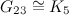 is a complete graph.
is a complete graph.
- In [2] it is claimed that the spectrum problem for
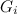 -designs where
-designs where 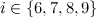 in the case where
in the case where 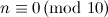 is settled in [17]; however, it seems likely that this is a typographical error. A likely intended reference is [11], as it is stated in [2] that
is settled in [17]; however, it seems likely that this is a typographical error. A likely intended reference is [11], as it is stated in [2] that 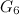 ,
, 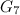 ,
, 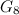 and
and 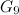 are dragons and these graphs are the topic of [11] (see Theorem 3 in the section on Miscellaneous graphs). However, the definition of dragons excludes the graphs
are dragons and these graphs are the topic of [11] (see Theorem 3 in the section on Miscellaneous graphs). However, the definition of dragons excludes the graphs 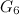 and
and 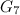 . Thus, the results in [11] settle the case
. Thus, the results in [11] settle the case 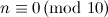 only for
only for 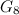 and
and 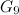 , and the case
, and the case 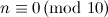 remains open for
remains open for 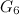 and
and 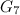 . Although Bermond et al [2]
describe a method which may be used to settle this case, the details
are not all included in their paper; however, the necessary designs are
constructed in [1].
. Although Bermond et al [2]
describe a method which may be used to settle this case, the details
are not all included in their paper; however, the necessary designs are
constructed in [1].
- Bermond et al [2] completely settle the spectrum problem for
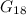 , except that the existence of a
, except that the existence of a 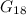 -design of order
-design of order 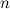 is left unresolved for
is left unresolved for 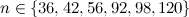 . Heinrich's survey [9] omits the case
. Heinrich's survey [9] omits the case 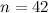 from the list of unresolved cases. In 2004, Li and Chang [14] constructed
from the list of unresolved cases. In 2004, Li and Chang [14] constructed 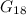 -designs of order
-designs of order 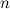 for
for 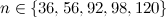 , and based on the list in [9] claimed to have finished the problem. A
, and based on the list in [9] claimed to have finished the problem. A 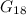 -design of order
-design of order 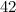 is constructed in [1].
is constructed in [1].
- It is worth noting that [16] contains an unfortunate error in the statement of a lemma. The lemma states that the existence of
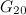 -designs of order
-designs of order 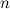 for all
for all 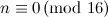 is implied by the existence of
is implied by the existence of 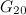 -designs of order
-designs of order 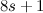 for various values of
for various values of  , but the actual proven result requires
, but the actual proven result requires 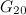 -designs of order
-designs of order 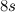 . This (unproven) result is incorporated in [9] and then used in [5] to (incorrectly) establish the existence of
. This (unproven) result is incorporated in [9] and then used in [5] to (incorrectly) establish the existence of 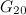 -designs of order
-designs of order 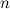 for all
for all 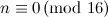 .
.
- The existence of a
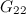 -design of order
-design of order 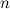 for all
for all 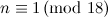 except for twelve unresolved cases is stated in [9]. Although this result is now known to be true, a proof is not given in any of the references cited in [9]. In [15], these twelve (previously) unresolved cases are settled, but it seems the first published complete solution of the case
except for twelve unresolved cases is stated in [9]. Although this result is now known to be true, a proof is not given in any of the references cited in [9]. In [15], these twelve (previously) unresolved cases are settled, but it seems the first published complete solution of the case 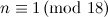 is in [8].
is in [8].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Adams, P., Bryant, D., and Buchanan, M. A survey on the existence of G-designs, J. Combin. Des. 16, 373–410 (2008).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Bermond, J. -C., Huang, C., Rosa, A., and Sotteau, D. Decomposition of complete graphs into isomorphic subgraphs with five vertices, Ars Combin. 10, 211–254 (1980).
- ↑ Blinco, A. Decompositions of complete graphs into theta graphs with fewer than ten edges, Util. Math. 64, 197–212 (2003).
- ↑ Bryant, D. and El-Zanati, S. Graph decompositions, CRC Press Series on Discrete Mathematics and its Applications, The CRC handbook of combinatorial designs, ed. 2, CRC Press, 477–486 (2007).
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Chang, Y. The spectra for two classes of graph designs, Ars Combin. 65, 237–243 (2002).
- ↑ Colbourn, C. J., Ge, G., and Ling, A. C. H. Graph designs for the eight-edge five-vertex graphs, Discrete Math. 309, 6440–6445 (2009).
- ↑ Colbourn, C. J. and Wan, P. Minimizing drop cost for SONET/WDM networks with 1 \over 8 wavelength requirements, Networks, 37, 107–116 (2001).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Ge, G. and Ling, A. C. H. On the existence of (K_5\sbs e)-designs with application to optical networks, SIAM J. Discrete Math. 21, 851–864 (2007).
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Heinrich, K. Graph decompositions, CRC Press Series on Discrete Mathematics and its Applications, The CRC handbook of combinatorial designs, ed. 1, CRC Press, 361–366 (1996).
- ↑ Huang, C. Balanced graph designs on small graphs, Utilitas Math. 10, 77–108 (1976).
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Huang, C. and Schönheim, J. Decomposition of K_n into dragons, Canad. Math. Bull. 23, 275–279 (1980).
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Kolotoglu, E. The Existence and Construction of (K_5\setminus e)-Designs of Orders 27, 135, 162, and 216, J. Combin. Des. (to appear),
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 G. Ge S. Hu, K. E. and Wei, H. A complete solution to spectrum problem for five-vertex graphs with application to traffic grooming in optical networks, J. Combin. Des. 23, 233 (2015).
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Li, Q. and Chang, Y. Decomposition of lambda-fold complete graphs into a certain five-vertex graph, Australas. J. Combin. 30, 175–182 (2004).
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Li, Q. and Chang, Y. A few more (K_v,K_5\sbs e)-designs, Bull. Inst. Combin. Appl. 45, 11–16 (2005).
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Rodger, C. A. Graph decompositions, Matematiche (Catania), 45, 119–139 (1991) (1990).
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Rosa, A. and Huang, C. Another class of balanced graph designs: balanced circuit designs, Discrete Math. 12, 269–293 (1975).
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 H. Wei, H. S. and Ge, G. Traffic grooming in unidirectional WDM rings with grooming ratio 9, Preprint,
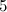 vertices
vertices